Minimize the function f(x, y, z)=x^{2}y^{2}z^{2} subject to the constraints x2 y3 z=6 and x3 y9 z=9 Video Transcript So the question is gonna look a little bit different We instead of having one constraints, we're gonna find extreme valueWhere A;B;C are constant It is a hyperbola if B2 ¡4AC > 0,15 14;¡ 5 14) satisfy the equation (1)Since f attains its minimum on the plane, by the Lagrange multipliers method, the point (57;
How To Eliminate The Arbitrary Function And Hence Obtain The Partial Differential Equation Z X Y F X 2 Y 2 Quora
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde-A partial differential equation has as many arbitrary functions as the highest order derivative The arbitrary functions as have the same role as the constants of integration in ODEs Boundary and initial conditions determine the arbitrary functioGet an answer for 'Show that z=ln((x^2) (y^2)) is a solution of Laplace's equation δ^2z/δx^2 δ^2/δy^2 = 0' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes



Differential Equations Complete Manual Pdf Document
Using ,multipliers x,y,z we get (xdx ydy zdz)/x(x^2 y^2 z^2) (xdx ydy zdz)/x(x^2 y^2 z^2) = dx/(2xz) 2(xdx ydy zdz)/(x^2 y^2 z^2) = dz/z Integrating, log(x^2 y^2 z^2) = logz logc2 (x^2 y^2 z^2) = zc2 Hence the required solution is f(c1,c2) = 0 = f(y/z, (x^2 y^2 z^2)/z) = 01(x 2y) f 2(x 2y) Answer 4@2z @x 2 = @2z @y 4 Form a PDE from the relation z = f 1(ax by) f 2(cx dy) Answer bd@ 2z @x2 (ad bc) @ z x y ac @2z @y2 = 0 5 Form a partial di erential equation from the relation z = f 1(2x 3y) f 2(4x 5y)Answer 15@ 2z @x2 22 @ 2z x y 8 @ z @y2 = 0 6 Form a partial di erentialX(y 2z 2)py(z 2x 2)q=z(x 2y 2) This equation of the form Ppq=R Here, P= x(y 2z 2) ,Q= y(z 2x 2) , R= z(x 2y 2) Use Lagrangian multipliers x,y,z, We get the ratio in (1) logx logylogz=log b Hence the general solution is, F(x
· 3Dplot of "x^2y^2z^2=1" Learn more about isosurface;F~ be the vector eld F~(x;y;z) = D z 2 y2; · ∂x 3 ∂x ∂y ∂x∂y 2 ∂yAns Auxiliary equation m 3 − 2m 2 − 4 m 8 = 0 m = 2,2,−2 Solution is z = f 1 ( y 2 x ) xf 2 ( y 2 x ) f 3 ( y − 2 x ) Part B(1)(i) Form a partial differential equation by eliminating arbitrary functions fromz = xf ( 2 x y ) g ( 2 x y )(ii) Solve p 2 y (1 x 2 ) = qx 2(2)(i) Solve x( z 2 − y 2 ) p y ( x 2 − z 2 ) q = z ( y 2
UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID MATEMATICAS PARA LA ECONOM IA II CURSO 19{ PROBLEMAS (SOLUCIONES ) HOJA 5 Optimizaci on 51 Hallar los puntos cr ticos de las siguiente funciones y clasi carlosRRand Lecture Notes on PDE's 2 Contents 1 Three Problems 3 2 The Laplacian ∇2 in three coordinate systems 4 3 Solution to Problem "A" by Separation of Variables 5 4 Solving Problem "B" by Separation of Variables 7 · The problem is I have to find all the possible combination of integers (x, y, z) that will satisfy the equation x^2 y^2 z^2 = N when you are given an integer N You have to find all the unique tuples (x, y, z) For example, if one of the tuple is



Partial Differential Equations


How To Eliminate The Arbitrary Function And Hence Obtain The Partial Differential Equation Z X Y F X 2 Y 2 Quora
Examples x2 2x 1 = 0 (algebraic equation) f(2x) = 2(f(x))2 −1 (functional equation) f′(t)t2f(t) = 4 (ODE) ∂u ∂x 3 ∂2u ∂x∂y −u ∂u ∂y (not an0709 · Form pde by eliminating arbitrary function xyz=∅(x^2y^2z^2)For f(x,y,z,a,b) = 0 differentiating wrto x,y partially and eliminating constants a,b we get a PDE Example 1 From the equation x 2 y 2 z 2 = 1 form a PDE by eliminating arbitrary



Pde Tutorial Sheet
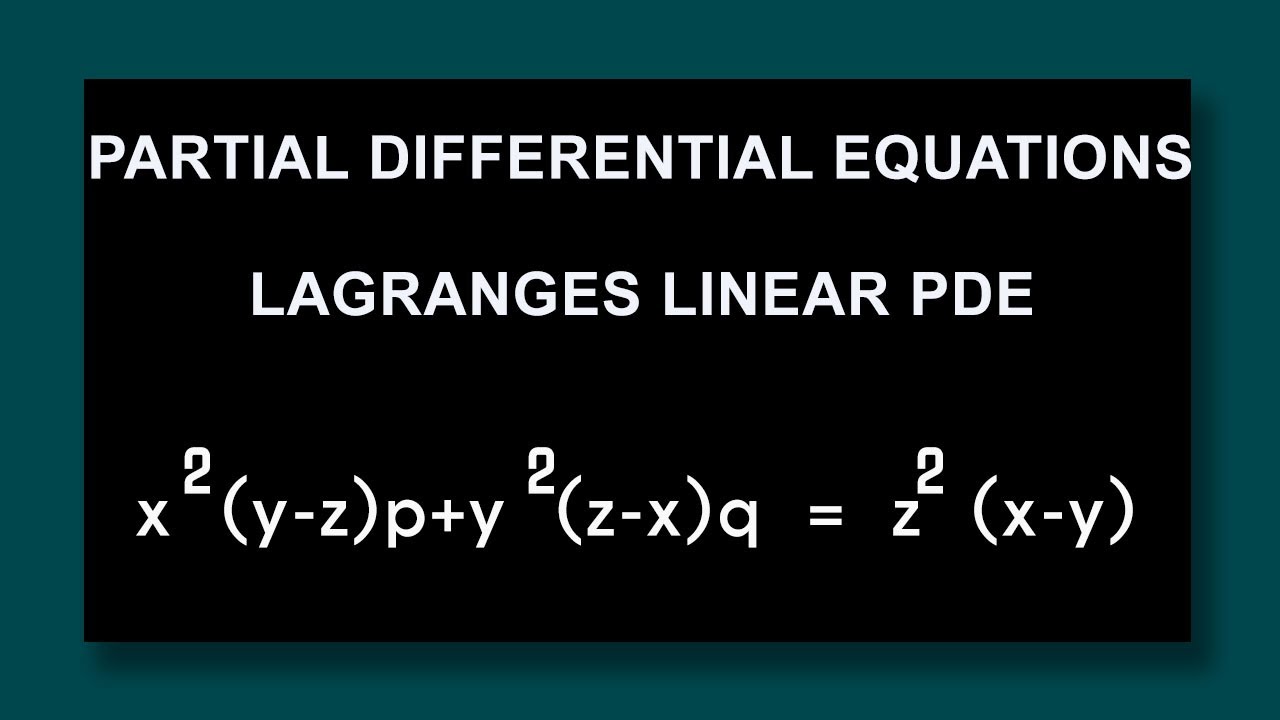


Partial Differential Equations Lagranges Linear Pde X 2 Y Z P Y 2 Z X Q Z 2 X Y Youtube
Plot f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 Extended Keyboard; · x y = z c = = log( ) log log v x y z c 2 1 2 ( ) The general solution is given by F(u,v) = 0 F(x1 y1,(x y)z1) = 0 2solve x2 (y z) y2 (z x)q = z2 (x y) solution Auxiliary equations are given by dz dy dx 2 ( ) y 2 ( z x ) z2 (x y) x y z = = 45Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition


Non Linear Fo Partial Differential Equations Ppt Download


Partial Differential Equation Notes
Get an answer for 'Find the integral of e^(x^2y^2z^2)^3/2 using spherical coordinates' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes15 14;¡ 5 14) has to be the nearest point 2 Consider the problem of minimizing the function f(x;y) = x2Find the Derivative d/dx x^2y^2z^2 By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is where Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is Combine terms


Mathematics 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Chapter 1 Maths 3
And with u(x, 0) = f(x) and ∂u / ∂y (x, 0) = g(x) for all values of x Even more phenomena are possible For instance, the following PDE , arising naturally in the field of differential geometry , illustrates an example where there is a simple and completely explicit solution formula, but with the free choice of only three numbers and not even one functionF(x 2 y 2 z 2 , 2x3y4z)=0 4Find the general solution of x(y 2z 2)py(z 2x 2)q=z(x 2y 2) Soln;F(x, y, z, p, q ) = 0 Example 5 Obtain the partial differential equation by eliminating „f„from z = ( xy ) f ( x 2 y 2 ) Let us now consider the equation z = (xy ) f(x 2 y 2) _____ (1) Differentiating (1) partially wrt x & y , we get p = ( x y ) f ' ( x 2 y 2 ) 2x f ( x 2 y 2 ) q = ( x y ) f ' ( x 2 y



1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Pdf Free Download



X 2p Y 2q X Y Zsolve The Following Pde Brainly In
A) \( \Large \phi \left(xyz, \frac{y}{z}\right)=0\) B) \( \Large \phi \left(\frac{y}{z},\frac{y}{x^{2}y^{2}z^{2}}\right) =0\) C) \( \Large \phi \left(\frac{y}{2Question F1(x,y,z) = X^2 y^2 z^2 −1 = 0 F2(x, Y, Z) = 2x^2 Y^2 − 4z = 0 F3(x,y,z) = 3x^2 −4yz^2 = 0 This System Can Be Concisely Represented As F(x) = 0, Where F(x) = (f1, F2, F3)T , X=(x,y,z)T And 0 = (0,0,0)T (transpose Written Because These Should Be Column Vectors) Using Matlab Starting With The Initial Condition X0 = (05, 05, 05)T , ImplementO comprimento e a largura de um retângulo foram medidos como $30$ cm e $24$ cm, respectivamente, com um erro de medida de, no máximo, $0,1$ cm Utilize as diferenciais para estimar o erro máximo cometido no cálculo da área do retângulo



Pdf Elementary Partial Differential Equations Simplified Theory Kwach Boniface Otieno Academia Edu



Partial Differential Equation Notes
Solves the PDE where f(t) = et for t 0, f(t) arbitrary for t > 0 In particular, the solution is not unique where x 2 y > 0, ie where jxj> jyj This is exactly the region in which the characteristic curves do not approach the yZ 2 −2 Z √ 4−x2 0 Z √ 4−x2−y2 0 y p x2 y2 z2 dz dy dx Solution (x = ρ sin(φ)cos(θ), y = ρ sin(φ)sin(θ), z = ρ cos(φ)) I Limits in θ θ ∈ 0π;We have x^2y^2=36z^2 and xy=10z, which gives (10z)^22xy=36z^2 or xy=3210zz^2 and xyz=32z10z^2z^3 Also, (xy)^2\geq4xy, We have x 2 y 2 = 3 6 − z 2 and x y = 1 0



18mat21 Module 3 Lct 04 Pde By Eliminating Function 1 Z Y 2 2f 1 X Logy 2 Xyz F X Y Z Youtube



Partial Differential Equations
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If u = f(r) , where r^2 = x^2 y^2 z^2 , then prove that ∂^2u∂x^2 ∂^2u∂y^2 ∂^2u∂z^2 = f^\" (r) 2rf (r)2xy;e p zcosz E Evaluate Z C F~d~r Solution The line integral is very di cult to compute directly, so we'll use Stokes' Theorem The curl of the given vector eld F~is curlF~= h0;2z;2y 2y2i To use Stokes' Theorem, we need to think of a surface whose boundary is the given curve C First, let's2 Substituting x = ‚;



One Dimentional Wave Eqn


What Is The Form A Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Functions F And G From Z F X 2 Y G X 2 Y Quora
Since 0 = u xy u x = (u y u) x, we can integrate at once with respect to xto obtain u yu= f(y)This is a rst order linear \ODE" in the variable y Introducing the integrating factor = exp R 1dy = ey, it becomes @y (e yu) = ef(y) Integrating with respect to ythis time yieldsI Limits in ρ ρ ∈ 0,2 I The function to integrate is f = ρ2 sin(φ)sin(θ) I = Z π 0 Z π/2 0 Z 2 0 ρ2 sin(φ)sin(θ) ρ2M11 Cálculo II Derivada direcional Gradiente Gradiente Selecione os exercícios por Dificuldade Fácil Médio Difícil Categoria Exercício Contextualizado Prática da Técnica Prática de Conceitos Demonstrações Problemas Complexos Outros



Partial Differential Equations With Matlab



Fom The Partial Differential See How To Solve It At Qanda
Let {eq}f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 {/eq} and let S be the level surface defined by f(x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at {eq}P_{0}(1,1,2)SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS FROM ASSIGNMENT 2 Problems 132d and 133d Statement Find general solutions of yu xy 2u x= xusing ODE techniques, as well as its particular solution satisfying the side conditions u(x;1) = 0 and u(0;y) = 06 OM4–VersionduApril1,09 2 Limitesetcontinuité Exercice21 Soitflafonctiondéfiniepar f(x,y) = 2xy−y2 x 2 y Étudier la limite quand (x,y) tend vers (0,0) de la restriction de f à la droite d'équationy= axavecadonnéMontrerquefn'apasdelimiteàl'origine Exercice22 Soitflafonctiondéfiniepar f(x,y) = x2y x4 −2x2y 3y2 si (x,y) 6= 00 si (x,y) = 0i) Étudier la limite



Pde Pdf Sma 2371 Partial Diffrential Equations January 4 1980 Course Outline 1 Surfaces And Curves In Three Dimensions 2 Simultaneous Dierential Course Hero



Assignment 5 Pde
0121 · Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeY = 3‚ 2 and z = ¡‚ 2 in the equation 2x 3y ¡ z ¡ 5 = 0, we obtain that ‚ = 5 7 and hence ‚ = 5 7 and (x;y;z) = ( 5 7;Wegen z2 < 1 sind die ersten beiden Zeilen genau f¨ur x = y = 0 erfullt Mit diesen Werten von¨ x und y ist k~vk 2 = z 2 und damit 2zk~vk z 3 − z = z(3z 2 − 1)



Pdf The Solution Of The Variable Coefficients Fourth Order Parabolic Partial Differential Equations By The Homotopy Perturbation Method


Non Linear Fo Partial Differential Equations Ppt Download
F(x,y,z) x^2y^2z^2 here are the intervals (x^2y^2)^(1/2)< Z < (18x^2y^2)^(1/2) 0 < X < (9y^2)^(1/2) 0 · Verify GDT for vector F = (x^2 yz)vector i (y^2 zx)j (z^2 xy)k taken over the rectangular parallelepiped 0 ≤x ≤ a, 0 ≤ y ≤ b, 0 ≤ z ≤ c3dprinting, solidworks f(0,0,0) is 0, not 1 (the isosurface level), so you only get points drawn completing the cones if there are enough points near the origin that happen to have value 1 But when you switch to linspace(,,), the closest coordinates to the origin are at about 105, leaving a gap of about 21



The Graph Of The X Y Z 0 Plane Download Scientific Diagram



Sma 2371 Pde Notes
Letf(x,y,z) = x^2y^2z^2 Calculate the gradient of f Calculate ∫_C(Fdr) where F(x,y,z)=(x,y,z) and C is the curve parametrized by r(t)=(3cos^3(t), 2sin^5(t), 2cos^13(t) for 2π≤t≤3πI Limits in φ φ ∈ 0,π/2;1) z = f(x 2 y2) Differentiating z partially w rt x and y, f x y y y z f x y x q x z p '(2 2)2 , '(2 2)2 p /q = x / y or y p –x q=0 as the pde (2 ) z = f ( x ct ) g (x ct) Differentiating z partially with respect to x and t, '( ) '( ), "( ) "( ) 2 2 f x ct g x ct x z f x ct g x ct x z Thus the pde is (3 ) x y z = f(x


How To Eliminate The Arbitrary Function And Hence Obtain The Partial Differential Equation Z X Y F X 2 Y 2 Quora



Differential Equations Complete Manual Pdf Document
I have a function f(x,y,z) = x^2 y^2 z^2 and I'd like to graph the surface defined by the equation f(x,y,z) = 1 When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;PDE ut = c2uxx, 0 < x < L, (0,0), ie, D includes all the points falling inside the unit circle x2 y2 = 1 Suppose f 1(x,y) = x2 − y2 is a solution to the following boundaryvalue problemGujji Murali Mohan Reddy PDE Lecture notes Example 261 Find the integral surface of the linear PDE x (y 2 z) p ≠ y (x 2 z) q = (x 2 ≠ y 2) z which contains the straight line x y = 0, z = 1 Exercise 262 Find the general solution of Tutorial2 Find the integral surface of the linear PDE (x ≠ y) y 2 p (y ≠ x) x 2 q = (x 2 y



Partial Differential Equations Pdf Peatix



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download
Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange2 Lecture 1 { PDE terminology and Derivation of 1D heat equation Today † PDE terminology † Classiflcation of second order PDEs † Derivation of 1D heat equation Next † Boundary conditions † Derivation of higher dimensional heat equations Review † Classiflcation of conic section of the form Ax2 Bxy Cy2 DxEy F = 0;S is defined as a sphere However, when I type "S f(x,y,z) = 1" into the input bar, nothing is graphed and the algebra window shows S as an undefined



Solved Partial Differential Equations 2 Form The Partial Chegg Com



Tpde 2 Partial Differential Equation Rates
X^2y^2z^2xyyzzx=0 multiplying the RHS and LHS by 2 we get , 2 x^2y^2z^2xyyzzx =0 or, (xy)^2(yz)^2(zx)^2=0 since in LHS there are only squared terms,ie they cannot be negative Let \displaystyle{x},{y},{z} are three real and distinct numbers which satisfy the Equation \displaystyle{8} · 设方程F(xyz,x^2y^2z^2)=0确定了函数 1626 设Z=㏑(根号x根号y),证明:x乘以x的偏导 y乘以 3 已知u=f(x^2y^z^2)求一阶和二阶偏导数



Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations


Find The Product X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube



Numerical Solution Of Partial Differential Equations



Unit1 Partial Differential Equation Equations



Creating A Successful Cv Dk Publishing 09 Subtraction Equations



Example 22 Particular Solution Dy Dx Y Cot X 2x X2 Cot X



Get Answer I Want Detailed Solutions From This Questions Thanks Show Transtutors



Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Lagranges Pde Y 2 Z 2 X 2 P 2xyq 2zx Youtube



Partial Differential Equations



First Order Partial Differential Equation Wikipedia



1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Pdf Free Download



If X Xy Yz Z C Then Show That At X Y Z Del 2z Delx Del



If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y



Formation Of Partial Differential Equations



Solved Find All Second Order Partial Derivatives For The Chegg Com



If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Then Prove That X 2 Y 2 Z 2 D 2u Dx 2 D 2u Dy 2 D 2u Dz 2 1



Calc3 1001 By James Bardo Issuu



Mathematics Ii Tranquileducation



Pdf Engineering Mathematics Ii 15mat21 Surya Karthik Academia Edu



Module 2 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations



Exact Equations Example 3 Video Khan Academy


Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers


Mathematics 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solved An Equation Which Involves Partial Derivatives Of Chegg Com



Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



2 Partial Differentiation



Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy



If X 2 Y 2 Z 2 2 X Y Z 3 Find The Value Of 2x 3y 4z Youtube
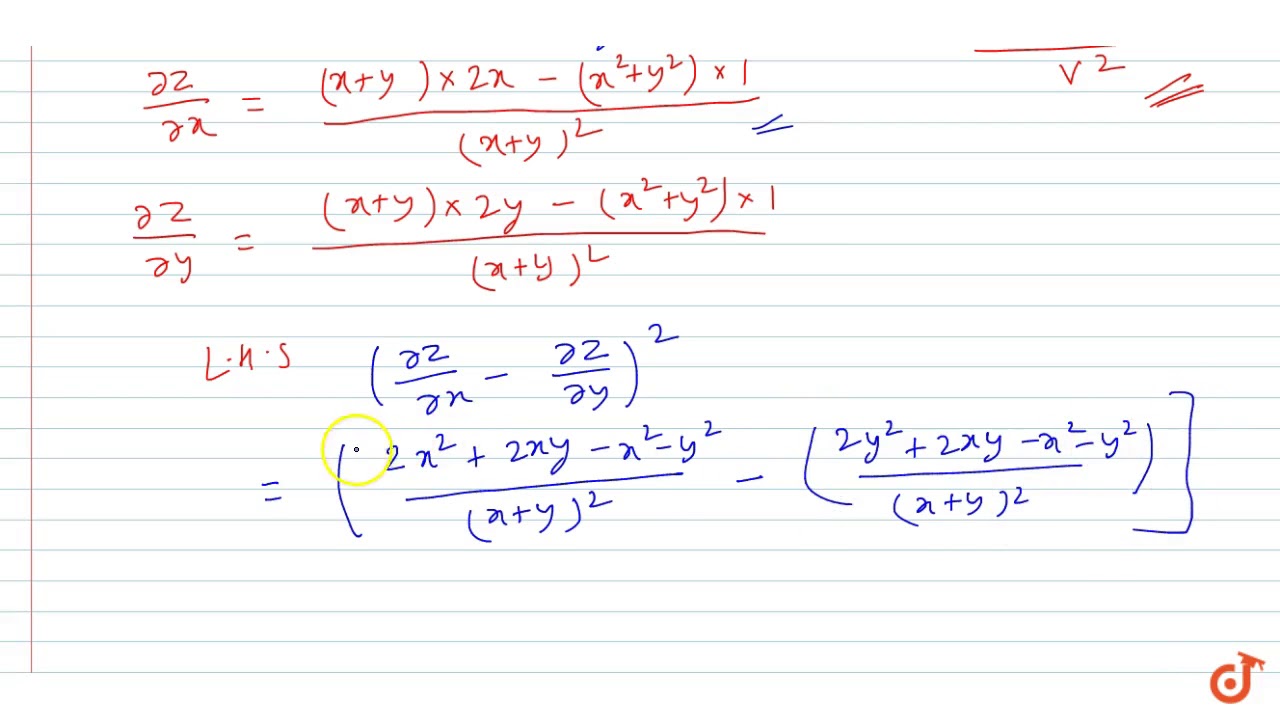


If Z X Y X 2 Y 2 Show That Delz Delx Delz Dely 2 4 1 Delz Delx Del Youtube



Fom The Partial Differential See How To Solve It At Qanda



1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Pdf Free Download



Partial Differential Equations



How Is Frac Dx Z X Y Frac Dy Z X Y Frac Dz X 2 Y 2 Equivalent To Frac Y Dx Xdy Zdz 0 Frac Xdx Ydy Zdz 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Partial Differential Equations



Advanced Engineering Mathematics Pages 651 700 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5


Mathematics 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Partial Differential Equation Notes



Ma 1 19 Pde Lecture 3 Partial Differential Equation Differential Equations



Fom The Partial Differential See How To Solve It At Qanda



11 Partial Differential Equations Partial Differential Equation Differential Calculus



Doc Partial Derivative Mcq S Assignement Innocentboy Nishant Academia Edu



Solving Systems Of Polynomial Equations Magma



Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



1 First Order Ordinary Differential Equations Pdf Free Download



Solved Questions 1 Consider The Function F X Y X2 Y Chegg Com



Chapter 1 Maths 3



Partial Differential Equation Notes



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿